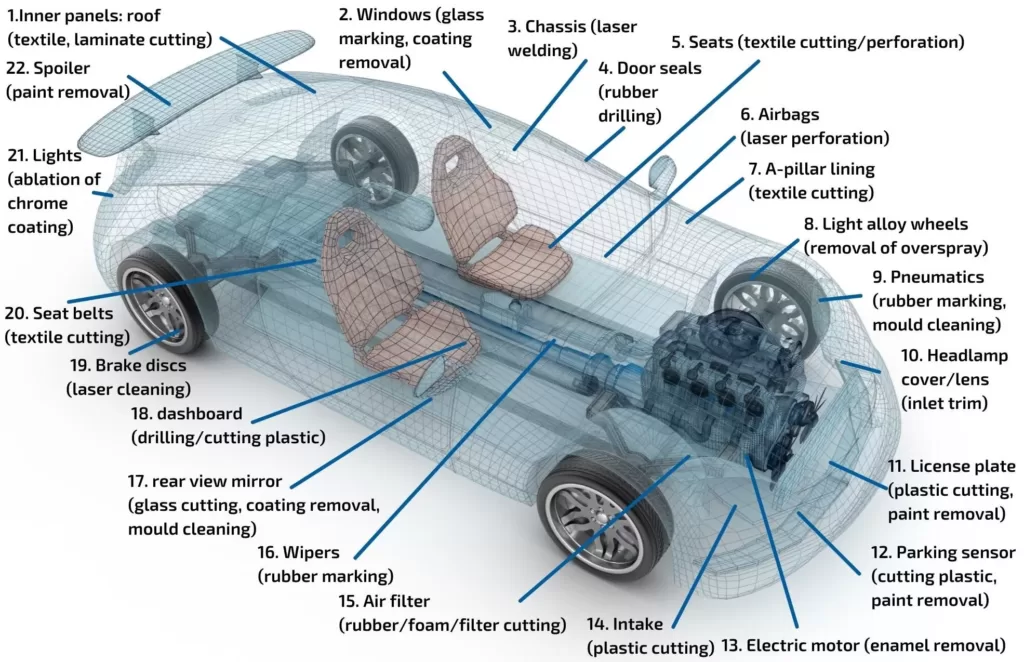
The ability of CO2 and fiber lasers to process a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, textiles, glass, and rubber, as well as less common materials used in the automotive industry like wood, leather, or carbon fiber, makes them among the most versatile tools available to the industry. For that reason, every aspect of the car—interior and exterior—has been laser-processed.
The output powers of fiber and CO2 lasers vary greatly, from watts to tens of kilowatts, and each system is employed in a multitude of activities. High power systems offer superior cutting, cleaning, and welding, whereas lower power systems are mostly utilized for marking and engraving.
Laser processing of plastics
Plastic parts are processed using lasers; some examples of particular applications include license plates, lamp covers, dashboards, bumpers, pillars, spoilers, and trims. Numerous types of plastic are employed:
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO)
- Polypropylene
- Polycarbonate
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
- Composite and laminate
Plastics can be painted or left uncoated, and they can be mixed with other materials to create reinforcement-containing structures like carbon or glass fiber-filled support structures, fabric-covered interior columns, and composite or veneered cladding panels.
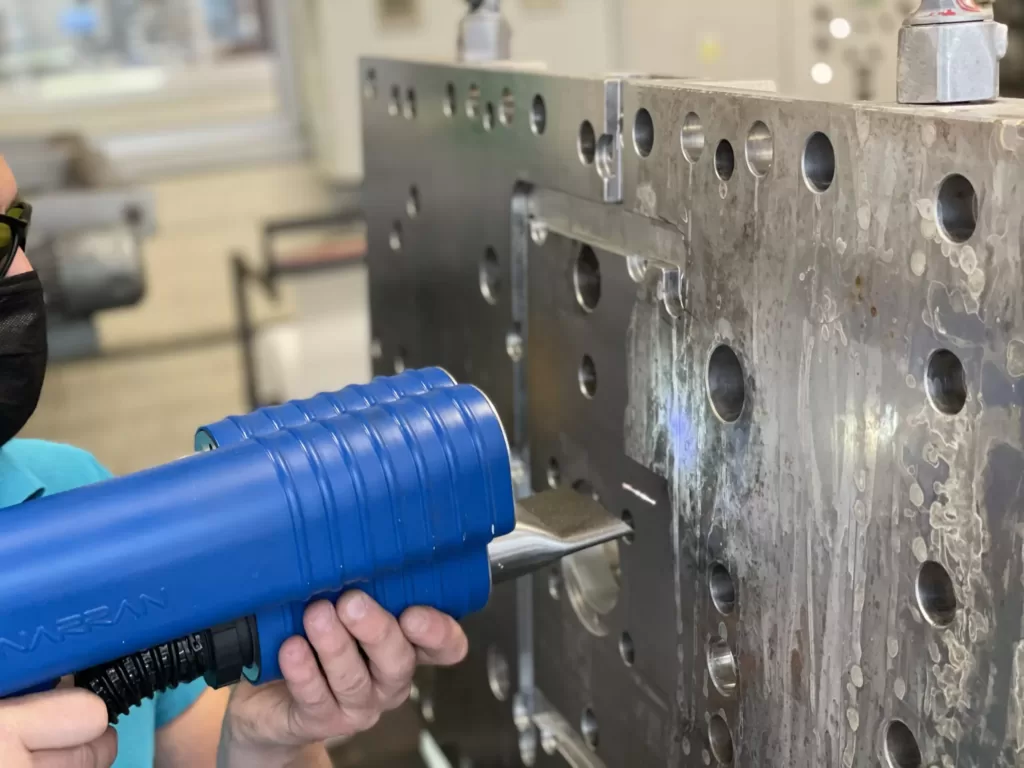
Fiber laser cleaning systems are also widely used to repair and clean injection molds for plastic parts. The primary reason for the growth in popularity of cleaning lasers over chemical or abrasive cleaning lies in the gentleness, associated high process repeatability, low operating costs, significantly higher system mobility, environmental friendliness, and the absence of the need to work with contaminated waste/cleaning media.

Lasers can be used to cut or drill holes for mounting points, lights, switches, parking sensors, and other components, as well as to degrade or trim excess plastic left over from the injection molding process. Headlight housings and lenses made of clear plastic often require laser trimming to remove the protrusions of waste plastic left after injection molding.
Plastic cutting operations are typically carried out with laser power from 80W upwards, depending on the time available to complete the task; our Narran OEM Veles series are suitable for these applications. When assessing the total cycle time for a set of operations, handling time must be taken into account so that laser power can be selected accordingly. Of course, handling requirements can be complex, and cutting operations often require the three-dimensional movement of the laser beam or part.
Surface cleaning/texturing
Laser technologies are not only used in the automotive industry for cutting, drilling, and trimming. Laser ablation also offers several applications in automotive manufacturing. Examples include surface treatment or removal of paint, rust, and other unwanted surfaces from selected areas of metals or composite, and it also finds use in cleaning injection molds and parts. This is often necessary when a part is to be adhesively bonded to a painted surface; it may be necessary to remove the top coat of paint or roughen the surface to promote good adhesion.
The cleaning lasers also achieve high efficiency in surface preparation for welding, soldering, painting, and cleaning of finished welds. The laser delivers just enough energy to remove the unwanted surface without damaging the material. Precise geometries can be easily realized, controlling ablation depth and surface texture, and changing ablation patterns as needed with minimal effort.

